SEO
Using Google Analytics for SEO performance
Using Google Analytics for SEO performance
"If you can't measure it, you can't improve it."
Techniques to help analyse your website using the new Google Analytics 4. Tips, hints and advanced guides. Or get us to do it for you.
Is social media a productive investment for your site? We can show you how to find out.
Setting up GA4
You may already have Universal Analytics - you can setup Google Analytics 4.
Basic Measurements
Enhanced Measurement
Enhance how specific events are handled in Google Analytics 4
Tracking and Reporting Outbound Clicks
Creating Custom Conversion Events (Key Events)
Setting Up GA4 Google Analytics 4
Setting Up Google Analytics 4
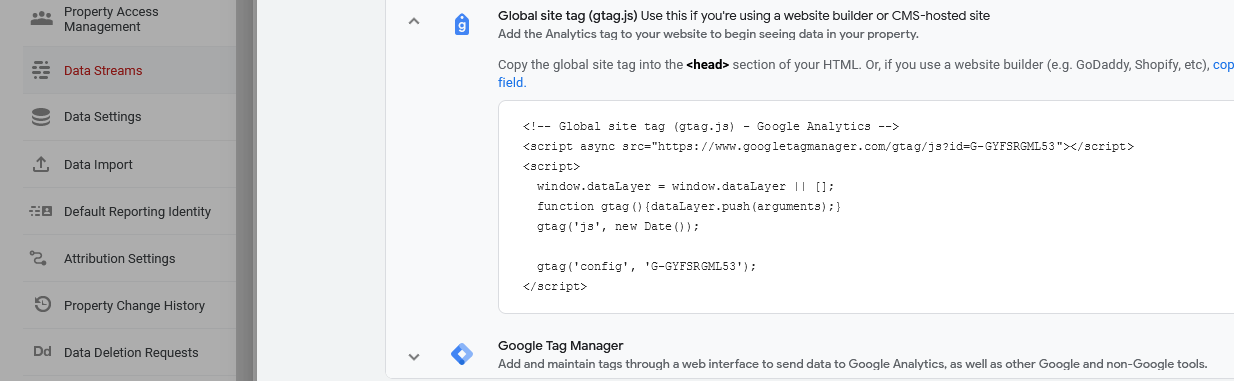
Latest Google Analytics UA stopped as of July 23 - However Google automatically sets up a GA4 property for you that seems to operate from your old UA settings. It is recommended to paste (replace the UA tag) in your website. How to get the new code to paste into your site-:
Admin>Data Collection and Modification>Data Streams>
View Tag Instructions>Installation Instructions>
Copy the tag instructions
The exact instructions are split between CMS and Manual Instructions. You end up with a G number which is your Measurement ID which uniquely identifies your website, blog or app.
One of the most compelling features of Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is how engagement is measured. Instead of Bounce-Rate in Universal, GA4 measures engagement out of the box, thus giving feedback on which pages and which Traffic Acquisition sources offer the best engagement. You can determine at a glance if your social media campaigns are effective.
Google Analytics 4 makes it easier to discover actionable, privacy-safe insights from across the customer journey. GA4 works with or without cookies or identifiers, so you can learn about your customers even with gaps in your data.
With machine learning at its core to automatically uncover insights from your data that help you predict and reach the customers who are most likely to convert.
Let's assume you have Google Universal setup already and want to update to Google Analytics 4. Setup GA4 as well as keeping Universal to ensure you retain your historical data. Also there are some useful reports in Google Universal and its integration with Google Console being valid reasons to retain it.
Steps in Setting Up Google Analytics 4
1: From Universal go to-:
Admin>GA4 Setup Assistant>
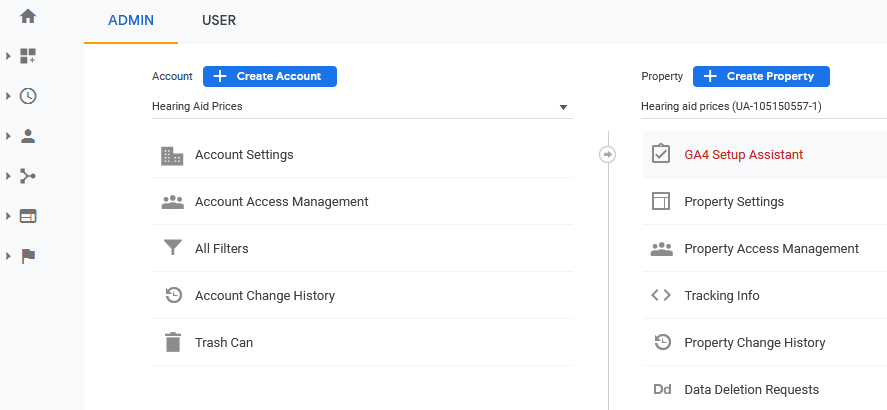
2: Click Get Started
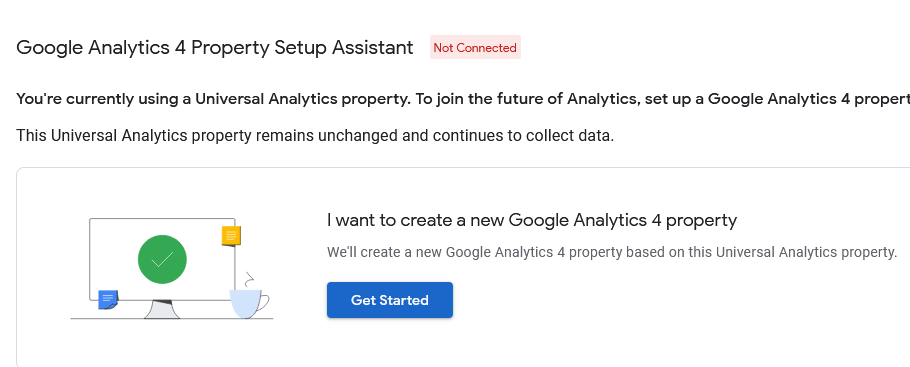
3: Click Create Property
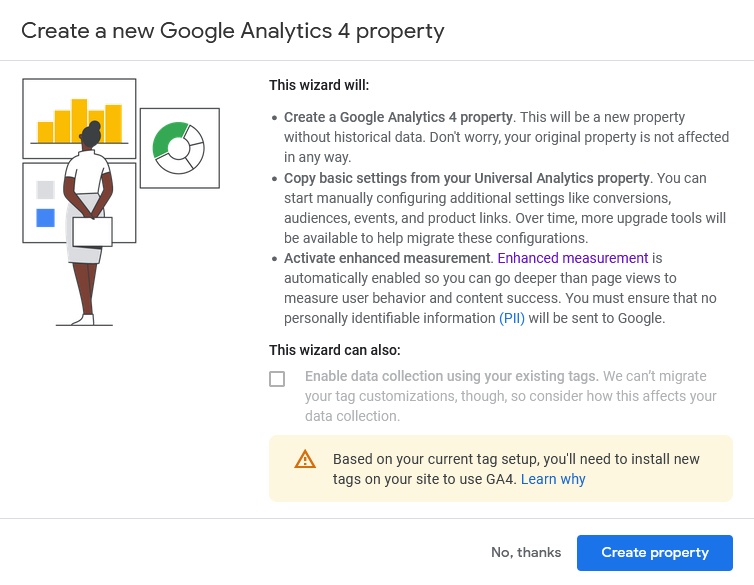
4: Click See your GA4 property
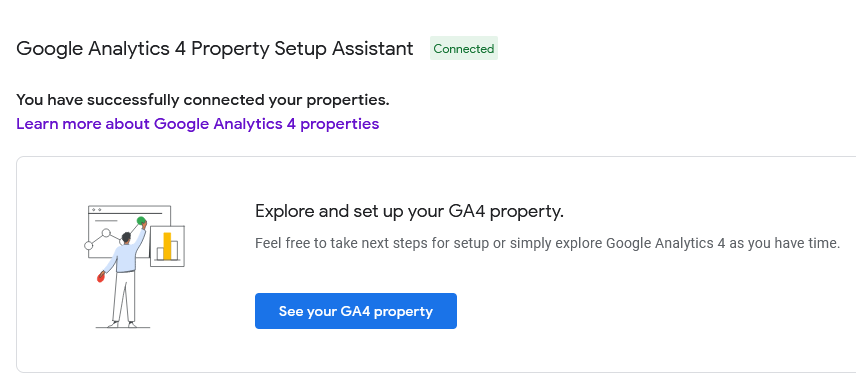
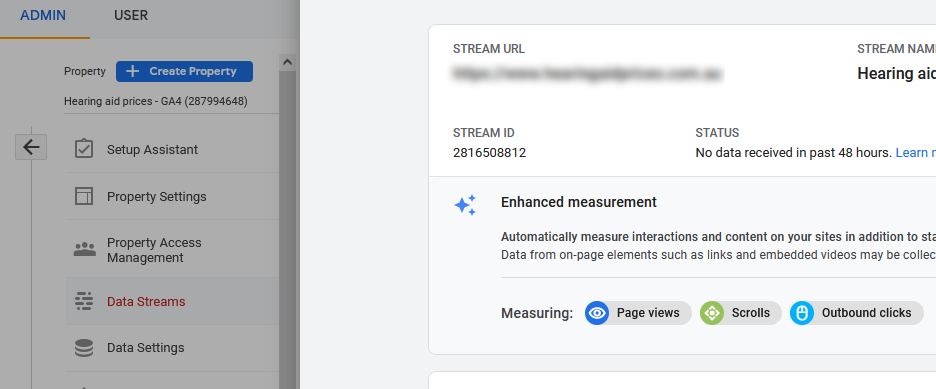
5: Confirm Data Streams (Enhanced Measurement)
6: Choose the appropriate Tag script and paste into every page of your site.
Congratulations!
You have have setup Google Analytics 4.
Take a look at live data and wait for data to be collected to explore the features and try some of the advanced techniques on this page.
Basic Measurements
Traffic Acquisition
User Engagement
Here is where we look at visitors to your website and analyse the results.
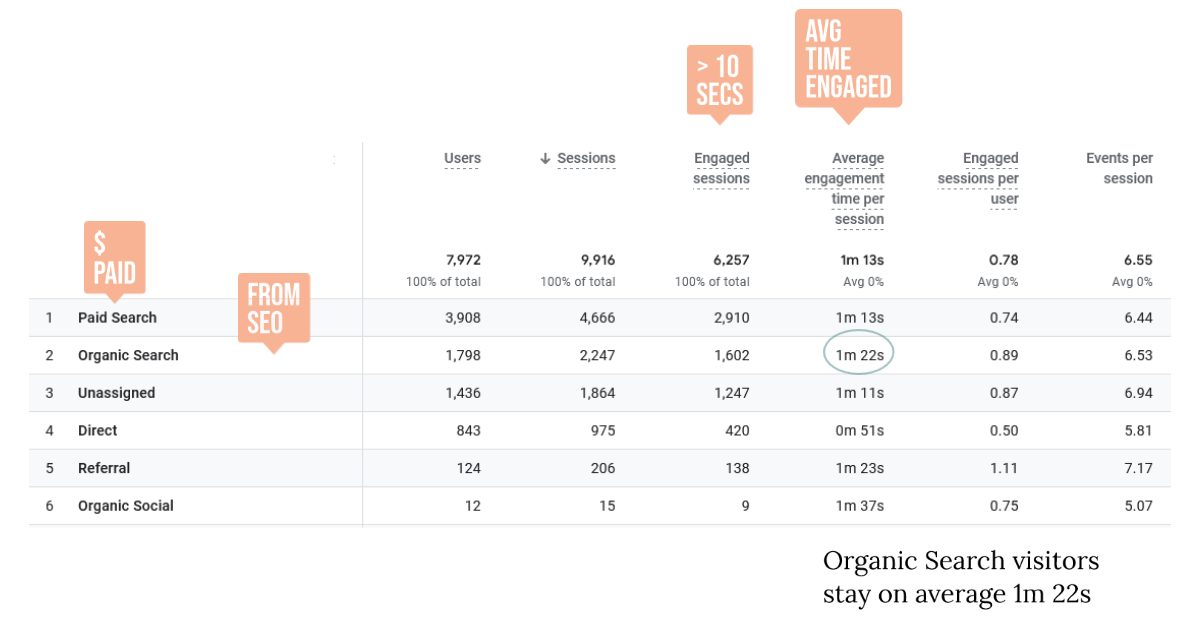
An engaged user in GA4 is any user that has been on the site for at least 10 seconds. If a user has been on the site for less than 10 seconds, they are defined as a bounce unless they have performed a key event or has at least 2 screen views.
Click to enlarge
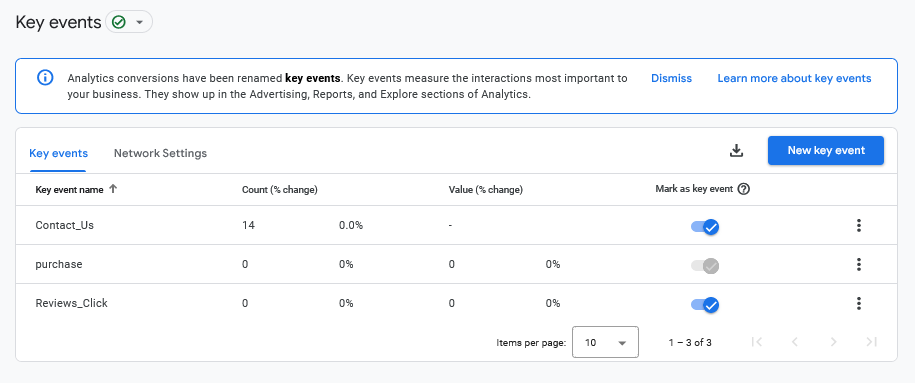
You can define a key event in GA4 via Admin>Data display>Key Events
Engagement time allows for screen sleep time. On a mobile device it captures the time in the foreground, to determine how a user is engaging with your content.
The engagement time will be different for the source of the user. Generally paid search has a lower engagement time than organic search.
Engagement will be different for various sites. Some sites are designed for quick access to pages. Depending on the context of the website you will make conclusions about its effectiveness.
Engaged Sessions Per User
Organic Search 1602/1798 = 0.89
A session in Google Analytics is simply a visit to your website. This is not users, a session could be the same person returning, even if the left your site up over the weekend a session would start again on their return. An Engaged Session is as determined above.
Engaged Sessions Per User is a good metric for the effectiveness of your content. You can also compare the level of engagement for different traffic sources. In this case we looked at Organic Search.
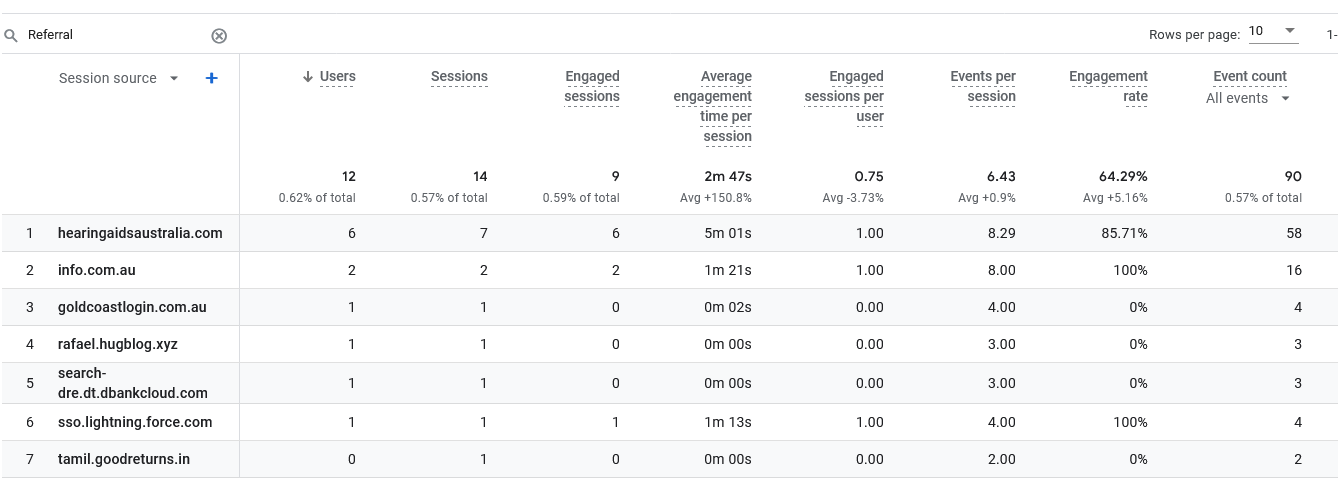
Referrals
Referral 138/124 = 1.11
Referrals are links from other sites. In this case some users had multiple sessions to get the Engaged Sessions Per User to 1.11
We can conclude that the sites linking into this site are adding real value.
In Universal Google Analytics the Referral sources are listed. Unfortunately in GA4 we can have to work a bit harder to find the actual sites that drove traffic to your site via links.
Viewing Referrals in GA4
We have to find the Traffic acquisition: Session source-:
1 Reports>Acquisition>Traffic acquisition
2 in the small Search box type: Referral
3 in the dropdown box select: Session source
Note in Step 2 we filtered by Referral - if we leave that blank it will show all sources including social media clicks recorded.
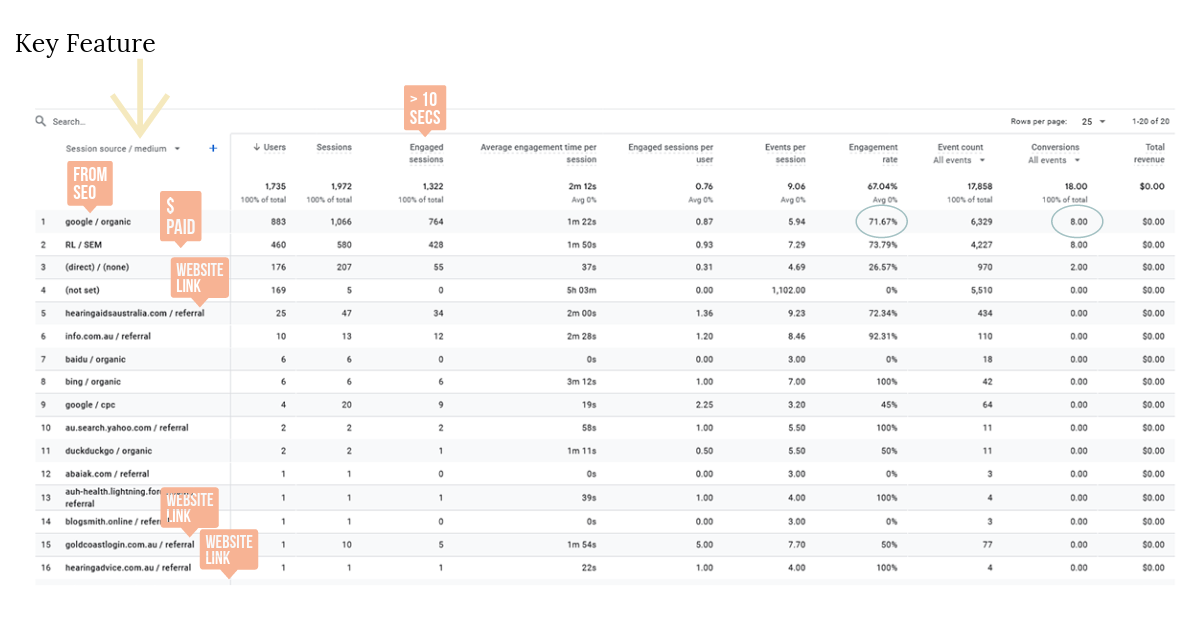
Key Feature of GA4 when analysing Traffic Acquisition
The Key to using Google Analytics 4 is to filter results to get information you need - refer to the arrow in the image and try it with your site and know more about your web traffic.

Engagement
Pages and Screens - Finding the best performing pages on your site
If you have a large blog with many pages there is a must use report to quickly identify the pages that are-:
1 Most Visited
2 Most Engaged
Reports>Engagement>Pages and screens>Filter by Page title and screen class
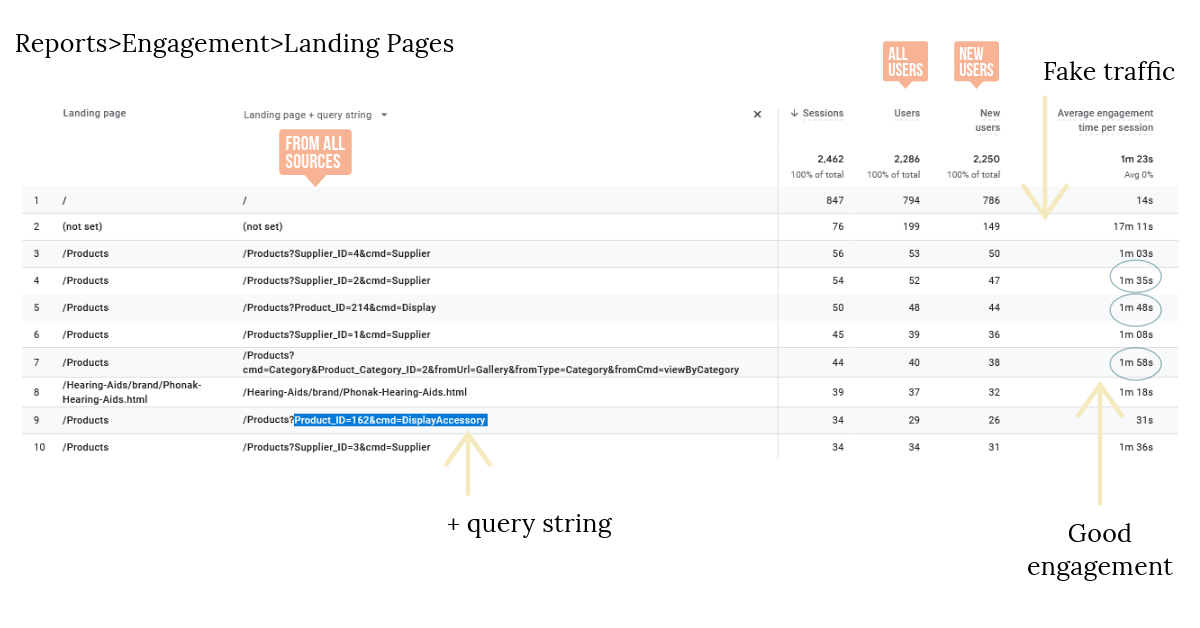
Landing Pages
Analysing Landing Pages Performance
Reports>Engagement>Landing page>Filter by Landing page + query string
This Google Analytics page (image above) gives data from all traffic sources ([Direct|SEM|Organic Search|Referrals etc) amalgamated. It offers a very quick analysis of which pages are performing well. Those with high numbers of traffic and good engagement are the best performers. Interpreting this information relies on knowledge of the pages and website in context with usual visitor behaviour for this type of site.
For example the / (home page) has low engagement (14 seconds), but in this case, that is good as this page simply acts as a lead in to product pages.
The image above shows Google Analytics for an eCommerce site with some hints as to what to identify and analyse-:
Query string
Query string is a useful additional filter which allows you to identify products or pages from a query string. So we know quickly which products are sparking interest and have the best engagement.
Fake traffic
Fake traffic is simply traffic with no engagement. These are often sites trying to hack or disrupt your site. Use security measures where necessary.
Engagement
Pages with good engagement indicate where you have good product listings or a collection of content that engages users.
Enhanced Measurement
Tracking and Reporting Outbound Clicks
There are automatically collected events in Google Analytics 4 (GA4). It is a programmable event driven model.
One of the events is a "click" which by definition is "each time a user clicks a link that leads away from the current domain". In this example we are going to enhance that click event to record clicks to external sources so they are reported.
We want to know specifically (in this case) how often a site clicks to Google My Business reviews and how often there is a click to an external booking site and see a report of the URLs and the count. When created you will see reports as per below-:
Engagement>Events>click>
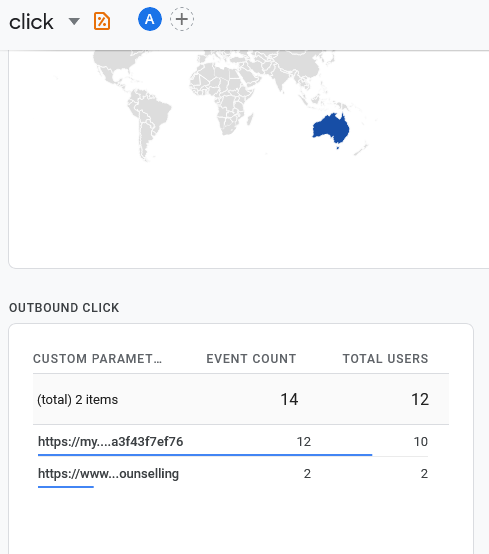
To see the Outbound Click report above we created a Custom Dimension (Configure>Custom Dimensions) named "Outbound Click" with the "Event" scope and the property parameter link/url. So when a link away from your site is clicked we are recording the url.
However the gotcha here is this will not be visible until there have been some of the events recorded. Hence take a note and return in a couple of days when some data has been recorded and you can then add this screen to your report (refer Creating Custom Dimension - note it may appear automatically). This is tricky because you see nothing initially until some events have been stored. So that makes it not available when you initially set it up.
Google explains this with 'you will see a value of "not set" for a custom dimension during the first 48 hours'.
Creating Custom Dimension (Definition)
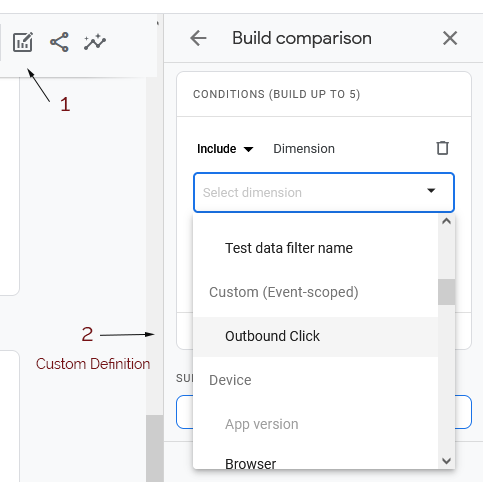
Preparation
Admin>Data Streams>Enhanced measurement>
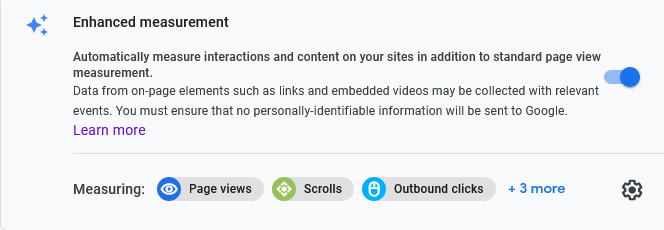
Ensure Enhanced measurement is switched on. Note we are recording Outbound clicks.
Value to SEO of recording Outbound clicks
Say for example you suspect that Google Reviews is playing a large factor in user behaviour on your site.
Recording Outbound clicks allows you verify this and hence determine the placement of Google Reviews on your site.
Say you have a site that is also promoting another site (a common SEO technique). You can measure precisely which pages (URLs) are being clicked.
Creating Key Events (previously called Custom Conversion Events)
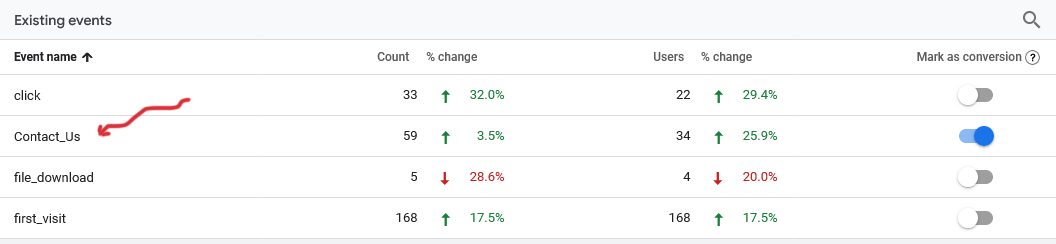
As an event driven model GA4 allows you to create custom events. So let's create a really simple one.
Admin>Events>Create event>
Note this is where you find and modify your existing events - yes if you have created an event some months ago and want to check what it contains you click the Create event button (note to self - that is why I write this stuff down in a place I can find).
1 Create (click)
2 Name it (Contact_Us)
3 Set the conditions
event_name equals page_view
page_location equals https://yourwebsite.com/page-location
4 Mark the new event as a conversion
Viewing your results
Admin>Events>
This is a simple example where a visit page_view to our Contact Us page triggered a conversion. Making more complex conversions follows the same process. Name the custom event and set the conditions based on events to see results which can be called a Conversion - previously a Goal in Google Analytics Universal.
We discuss Measuring the effectiveness of Web Forms where we can combine forms and hidden parameters to trigger Conversion Events. This would allow us to compare the effectiveness of pages and form formats.
Google Instructions for Custom Event Conversions

Click to enlarge
Google Page for Create or modify conversion events
Unique Tracking Codes UTM
A UTM tag are specific parameters added to a URL (in any order) that allow tracking of specific campaigns. For example you may want to track the effects of an email campaign and differentiate it from normal web traffic.
If you're setting up URL parameters for a Google Analytics 4 site, then you have to add at least one utm parameter, but you can add any utm parameter.
Source (utm_source)
Medium (utm_medium)
Campaign name (utm_campaign)
Term (utm_term)
Content (utm_content)
An example of tracking used by Jetstar on their Friday Frenzy email promotion-:
https://www.jetstar.com/au/en/friday-fare-frenzy?dealsorig=*&RMID=jstar.14092896&RRID=416857446&CID=############
&utm_source=jetmail
&utm_medium=email
&utm_campaign=20230922_acq_fff_au%7C_FFF_HG-2_A_QLD
Email campaigns are valuable to SEO because you can recycle content and people will often search for the article on your site at a later date. Tracking what is happening can be done in a number of ways. It is important to retain clarity in your campaigns so that you do not clutter up your data.
Track Site Search in GA4
Site searches can be internal or you can use Google's site: [operator] in Google searches -:
site:goldcoastlogin.com.au SEO Prices Gold Coast
Powerful internal site searches favour eCommerce sites and large blogs. We developed advanced search techniques to help with Save Our Spit which has over 300 unique articles. It allows special operators like + - * and "" to pinpoint information quickly. The following search would find articles that included the words Palaszczuk.
Palasz*

Save Our Spit - advanced smart search
GA4 allows you to view the words used in internal site searches. To set this up follow the steps from https://measureschool.com/track-site-search-in-ga4/. The steps they use work well, it would take a very long explanation here to include those steps.
By default GA4 records the URLs used but that would only give us a URL like http://www.saveourspit.com/No_Terminal/search/Search.jsp it would not include the actual search which in our case was http://www.saveourspit.com/No_Terminal/search/Search.jsp?cmd=Search&keywords=Palasz*
Advanced site searches can be used by advanced users and even people within an organisation that want quick access to public company information.
We could build an admin page to measure these statistics BUT why build that if GA4 already has the ability to be programmed to produce that information?
Viewing your internal site searches in GA4 (once setup)
This is an example of a custom report created to report on the search terms used-:
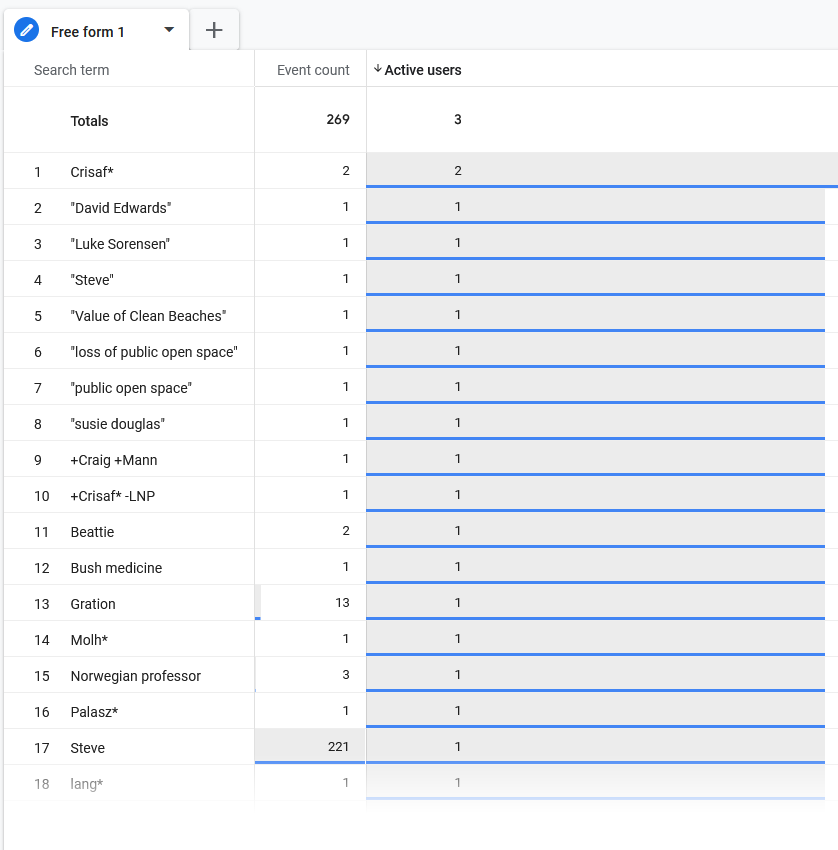
It tells us the terms used and the frequency and the number of active users [test data]
These reports are about viewing meaningful data over select periods. They are very powerful, and need to be setup properly to do this.
Linking GSC and GA4
When you link Google Search Console to Google Analytics you get really good insights into your search queries and the engagement coming from those queries. Specifically we can see which pages are getting a good engagement rate and which are not and need some improvements.
Steps
1 Log in to GA4: Sign in to your Google Analytics 4 account.
2 Go to Admin: Click the Admin gear icon in the bottom-left corner.
3 Select Search Console Links: In the Property column, scroll down and click Search Console Links under Product Links.
4 Initiate the link: Click the blue Link button in the top right corner.
5 Choose GSC account: Click Choose accounts and select the GSC property you want to link. Click Confirm.
6 Select web stream: Click Next, then choose the correct web data stream for your site from the list and click Next again.
7 Review and submit: Review the settings to ensure everything is correct, then click Submit.
It may take 24 hours or more to see the Queries and Google organic search traffic under the Search Console menu in GA4.
SEOs use software to get an insight into pages that are nearly getting clicks. It is also important to know definitively which pages are performing well via the engagement rate. We do not see an engagement rate in GSC but combined into GA we can gain deeper insights.
We also know precisely which pages are getting organic clicks from Google. We do not know what the query was, but we know the pages and the number of clicks.
A Gold Coast SEO and Web Developer